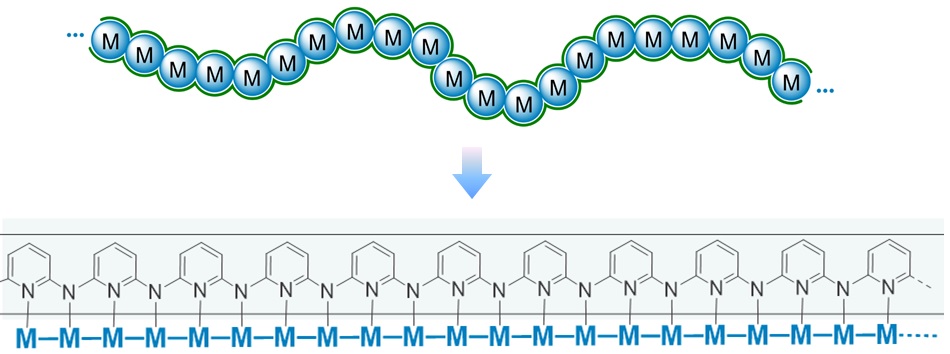
Over the past century, the development of polymer science has focused on polymers with backbones consisting of non-metallic atoms such as carbon, nitrogen and oxygen. However, metal elements accounting for more than 80% of the periodic table of elements have been rarely studied as backbones of polymers, thus realizing polymer backbones that are completely composed of metal atoms remains unavailable. We design and synthesize new polymers whose backbones are completely made from metal atoms, reveal the impact rules of their components and structures on properties, and achieve excellent electronic and mechanical properties. We may open a new direction at polymer science.
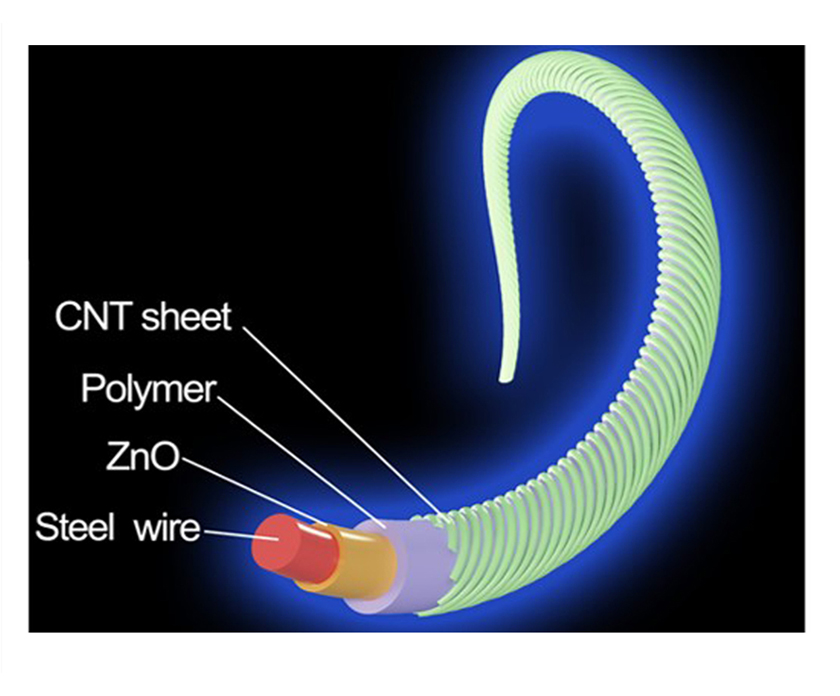
More than 5,000 years ago, ancient Chinese utilized natural fibers like silk to weave textiles, marking a significant milestone in human civilization. However, fibers still appear as a type of materials with the remaining functions of keeping people warm and comfortable. With the further revolution in information technology, it is urgent to transform the above fiber materials into fiber devices. We have thus integrated electronic function and fiber shape to create different types of fiber devices including solar cells, lithium-ion batteries, sensors, light-emitting devices, displays and integrated circuits with emphasis on charge transports on curved fiber surfaces. We have also realized continuous fabrications of fiber devices for real applications.
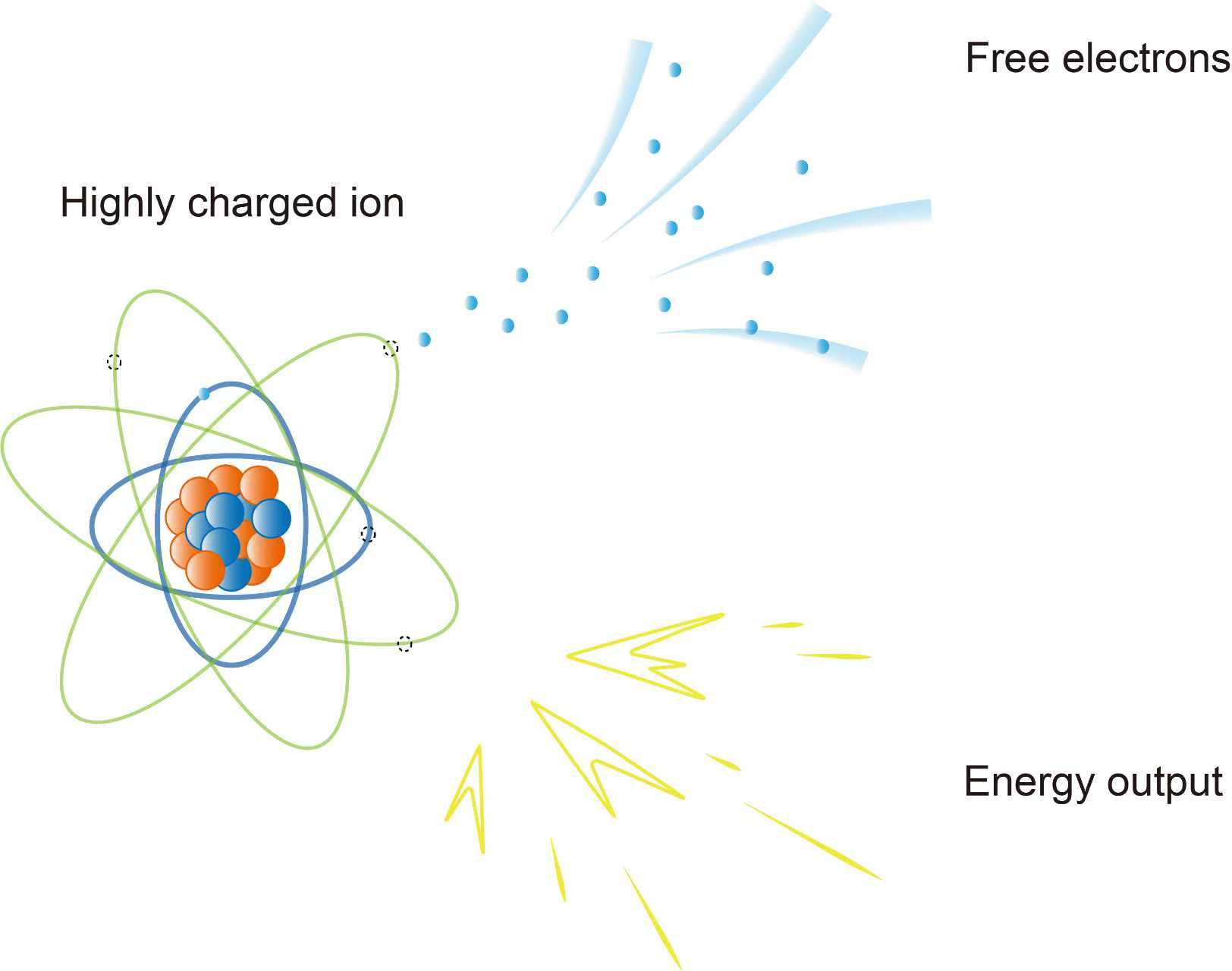
(1) Inner shell electrons for energy devices. For classic electrochemistry, both energy harvesting and converting devices utilize outermost electrons, resulting in low energy densities. We are exploring the transition from excited to ground states in inner shell electrons to release several orders of magnitude more energy. (2) Fractional element. According to the classic theory, the elements in the periodic table are organized by integers. We may discover non-integer elements named fractional element. (3) New learning paradigm. The traditional learning model needs repeated training to memorize and accumulate knowledge. Inspired by Chinese Wuxia novels that knowledge can be transferred from an experienced swordsman to a newcomer in minutes with their palms against each other, we are exploring a new learning pathway.